User Guide

As a student entrepreneur with a busy schedule, do you always find yourself missing an appointment/meeting with your clients or friends? Or can’t seem to find a way to easily recall details of a certain someone who is probably stored as one of your many contacts in your Excel sheet? Fret not, as we have designed an application called ContactSH just for you! It is a Desktop application for managing your contacts as well as tasks related to each of them. It boasts a highly effective search function and contact-task tracking system. It is also optimized for use via a Command Line Interface(CLI) that is similar in style as Linux CLIs, while still having the benefits of a Graphical User Interface (GUI). If you can type fast, you will be able to manage business tasks related to your contacts more efficiently than using other traditional GUI apps.
The Quick Start section shows you how to quickly get ContactSH up and running on your computer. If you are a new user, it is recommended to go through the instructions under Features one by one. If you are an experienced user, and just want to refer to the list of features, you may use the Table of contents to quickly navigate to the command of your choice.
Table of Contents
- Viewing details of instructions :
man - Adding a person :
add - Editing a person :
edit - Deleting a person :
rm - Listing all persons :
ls - Sorting persons by name:
sort - Locating persons by name :
find - Adding a task :
add - Editing a task :
edit - Deleting a task :
rm - Viewing tasks :
cat - Marking a task as done :
donetask - Marking a task as not done :
undotask - Setting the number of days before tasks are considered due soon :
reminder - Clearing the screen :
clear - Accessing the cache
- Saving the data
- Editing the data file
- Archiving data files
[coming in v2.0]
FAQ
Command Summary
Flag summary
Quick start
-
Ensure you have Java
11or above installed in your Computer. -
Download the latest
ContactSH.jarfrom here. -
Copy the file to the folder you want to use as the home folder for your ContactSH.
-
Double-click the file to start the app. The GUI similar to the below should appear in a few seconds. Note how the app contains some sample data.
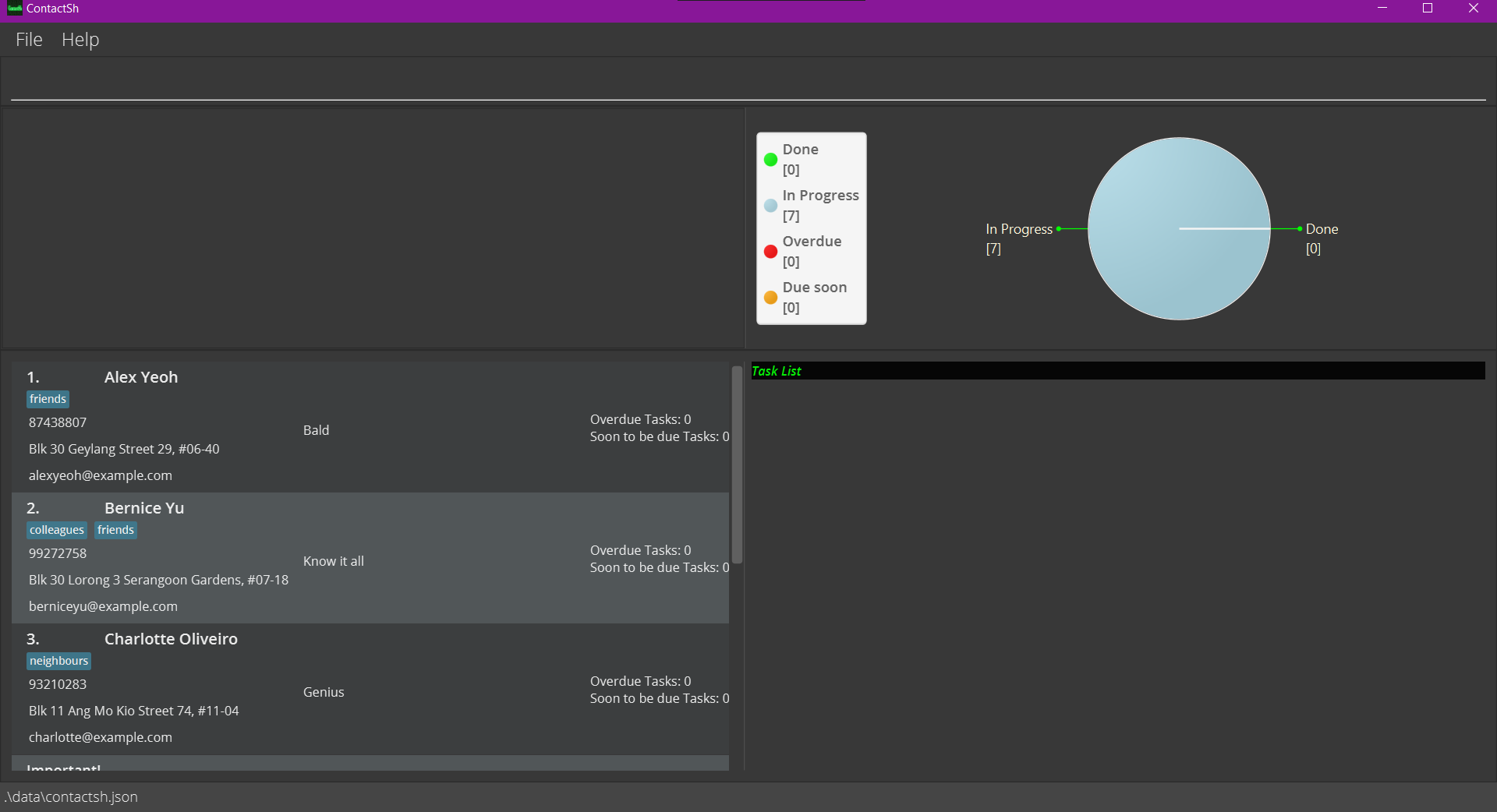
-
Type the command in the command box and press Enter to execute it. e.g. typing
manand pressing Enter will open the help window.
Some example commands you can try:-
ls: Lists all contacts. -
add -nJohn Doe -p98765432 -ejohnd@example.com -aJohn street, block 123, #01-01: Adds a contact namedJohn Doeto ContactSH. -
rm 3: Deletes the 3rd contact shown in the current list. -
rm -A: Deletes all contacts.
-
-
Refer to the Features below for details of each command.
-
Refer to the Flag Summary Table below for details on the flags used in the commands.
Features
![]() Notes about the command format:
Notes about the command format:
-
Words in
UPPER_CASEare the parameters to be supplied by you.
e.g. inadd -nNAME,NAMEis a parameter to be specified:add -nJohn Doe. -
Items in square brackets are optional parameters.
e.g-nNAME [-lLABEL]can be specified as-nJohn Doe -lfriendor-nJohn Doe. -
Items with
… after them can be specified multiple times including zero times.
e.g.[-lLABEL]…can be specified as `` (i.e. 0 times),-lfriend,-lfriend -lfamilyetc. -
Parameters can be in any order.
e.g. if the command format is-nNAME -pPHONE_NUMBER,-pPHONE_NUMBER -nNAMEis also acceptable. -
If a parameter is expected only once in the command format, but you specified it multiple times, only the last occurrence of the parameter will be accepted.
e.g. if you specify-p12341234 -p56785678, only-p56785678will be accepted.
There are a few exceptions to this which are the find command and the cat command. In such cases, if a parameter is expected only once and there are more than one standalone flag, the words after the first flag will be taken as keywords. -
Extraneous parameters for commands that do not take in parameters (such as
ls,exitandclear) will be ignored.
e.g. if you specifyls 123, the command will be interpreted asls.
Viewing details of instructions: man
Shows you details of instructions that can be used to navigate the app.
Format: man [COMMAND_NAME]
Notes:
-
If no
COMMAND_NAMEis entered, you will see a table of instructions, in a new window, that can be used to navigate the app. -
If you enter a valid
COMMAND_NAME, you will see the details of that command, which includes the format and taskName of the command.
Examples:
-
man sortShows the full details ofsortcommand as below.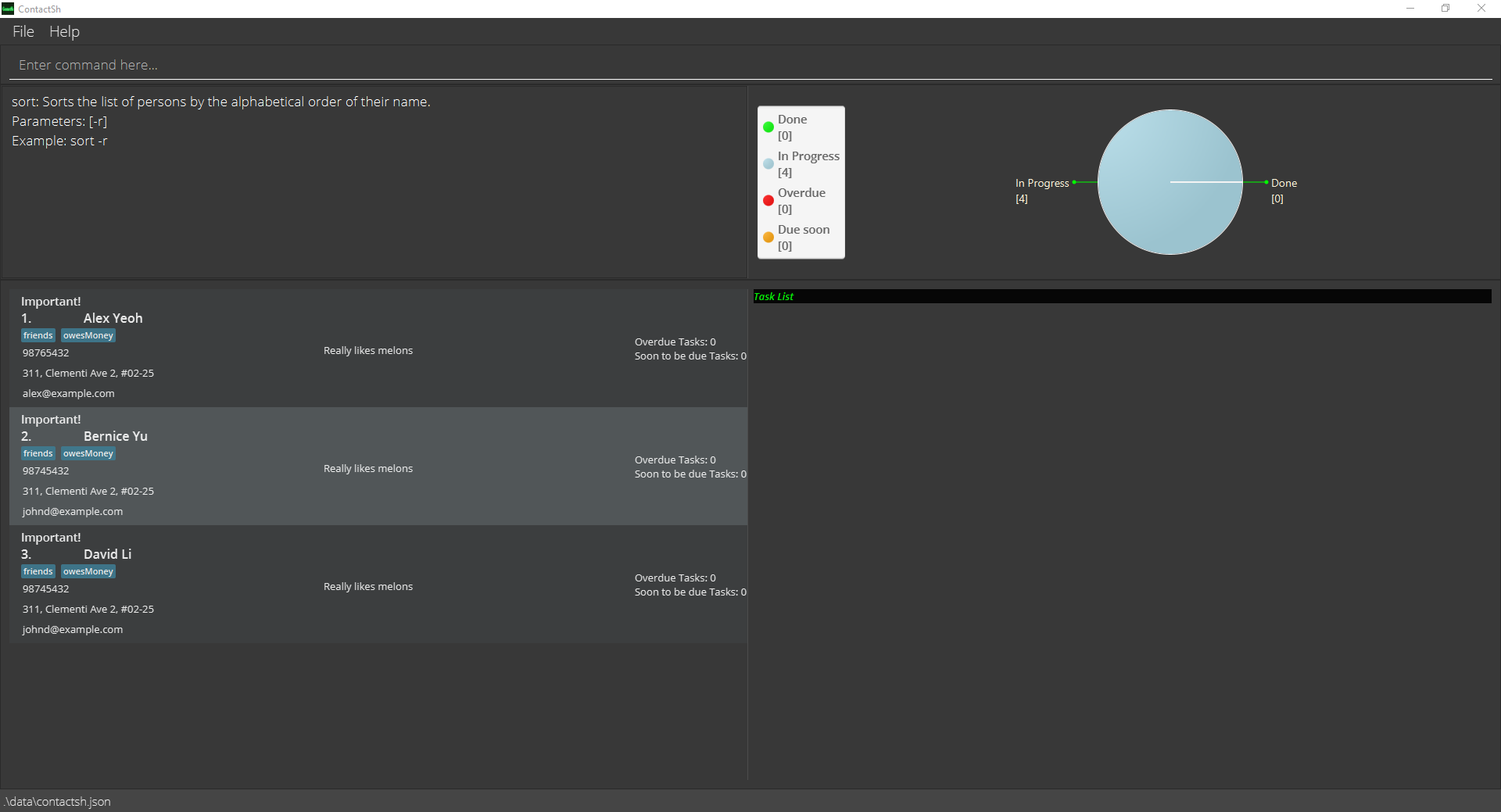
Adding a person: add
Adds a person to ContactSH.
Format: add -nNAME -pPHONE_NUMBER -eEMAIL -aADDRESS [-dDescription] [-lLABEL]... [-imptIMPORTANCE]
Notes:
-
Person in ContactSH are considered the same person if they have the same name. Duplicate person are not allowed in ContactSH.
-
IMPORTANCEis either “true” or “false” (Case insensitive)
Examples:
-
add -nJohn Doe -p98765432 -ejohnd@example.com -aJohn street, block 123, #01-01Adds a person with nameJohn Doe, phone number98765432, emailjohnd@example.com, addressJohn street, block 123, #01-01. -
add -nBetsy Crowe -lfriend -ebetsycrowe@example.com -aNewgate Prison -p1234567 -dBald -lcriminalAdds a person with nameBetsy Crowe, phone number1234567, emailbetsycrowe@example.com, addressNewgate Prison, labelcriminalandfriend, descriptionBald.
Editing a person: edit
Edits an existing person in ContactSH.
Format: edit INDEX [-nNAME] [-pPHONE] [-eEMAIL] [-aADDRESS] [-dDESCRIPTION] [-lLABEL]… [-imptIMPORTANCE]
Notes:
- Edits the person at the specified
INDEX.INDEXrefers to the index number shown in the displayed person list.INDEXmust be a positive integer less than or equal to 2147483647: 1, 2, 3, …, 2147483647 - At least one of the optional fields must be provided.
- Existing values will be updated to the input values.
- When editing labels, the existing labels of the person will be removed (i.e editing labels overwrites previous labels).
- You can remove all the person’s labels by typing
-lwithout specifying any labels after it. -
IMPORTANCEis either “true” or “false” (Case insensitive)
Examples:
-
edit 1 -p91234567 -ejohndoe@example.comEdits the phone number and email address of the 1st person to be91234567andjohndoe@example.comrespectively. -
edit 2 -nBetsy Crower -lEdits the name of the 2nd person to beBetsy Crowerand removes all their existing labels.
Deleting a person: rm
-
Deletes a specified person from ContactSH.
Format:
rm INDEXNotes:
- Deletes the person at the specified
INDEX. -
INDEXrefers to the index number shown in the persons list displayed. -
INDEXmust be a positive integer less than or equal to 2147483647: 1, 2, 3, …, 2147483647
Examples:
-
lsfollowed byrm 2deletes the 2nd person listed in ContactSH. -
find -n Betsyfollowed byrm 1deletes the 1st person in the results of thefindcommand.
- Deletes the person at the specified
-
Deletes all persons from ContactSH.
Format:
rm -A
Listing all persons: ls
Shows a list of all persons in ContactSH.
Format: ls
Sorting persons by name: sort
Sorts persons by the alphabetical order of their name.
Format: sort [-r]
Notes:
- The default sort with no options provided displays a list of persons sorted in ascending ASCII alphabetical order of their name.
- If the optional
-rflag is provided, a list of persons sorted in reverse order is displayed.
Locating persons: find
Finds persons whose attribute contains any of the given keywords.
Format: find [-n NAME] [-p PHONE] [-e EMAIL] [-a ADDRESS] [-d DESCRIPTION] [-l LABEL] [-tn TASK_NAME]
Notes:
- A space is necessary between a command word, a flag and a keyword.
- Only 1 attribute can be specified per find command.
- The search is case-insensitive. e.g. hans will match Hans
- The order of the keywords matters. e.g. Hans Bo will not match Bo Hans
- Only the specified attribute is searched.
- At least one of the optional fields is required.
- Abbreviations will be matched e.g. Han will match Hans
- Persons matching ALL the keywords will be returned. e.g. A Y will return Alex Yeoh, Alexandra Yee, but not Aileen
- Only one flag is allowed per command. e.g.
find -n Alexis fine, butfind -n Alex -n Bernicewill search with the keywords “Alex -n Bernice”.
Examples:
-
find -n AlexFinds all people whose name matches the keyword “Alex”.
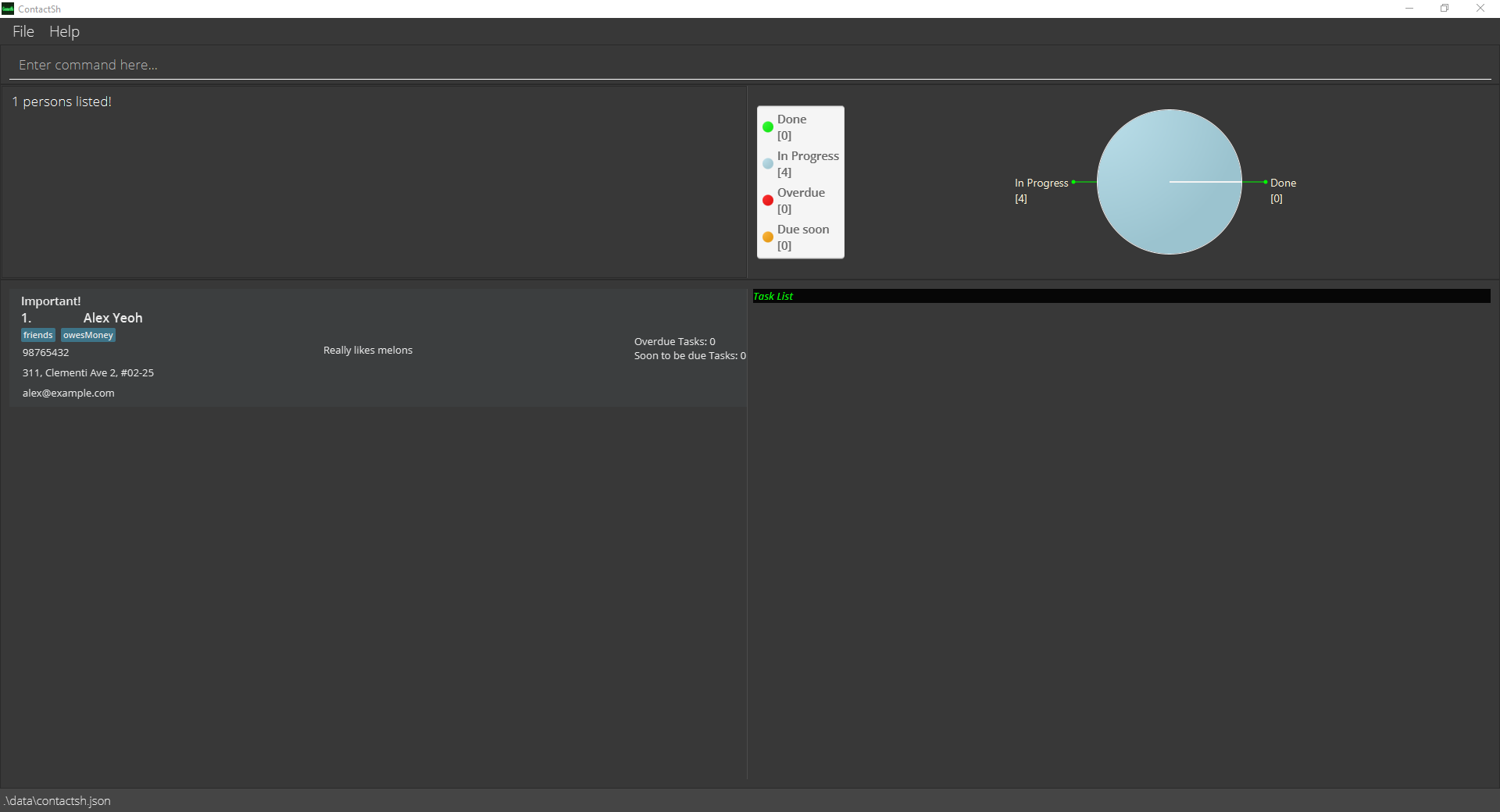
find -n alex will match a person with
the name “Alex Yeoh”. However, find -n lex and find -n yeo alex will not match the same person with the name
“Alex Yeoh”.
Adding a task: add
Adds a task to the current list of tasks attached to a person.
Format: add INDEX -tnTASK_NAME [-tdTASK_DATE] [-ttTASK_TIME] [-taTASK_ADDRESS]
Notes:
- Adds a task to the person at the specified
INDEX.INDEXrefers to the index number shown in the persons list displayed.INDEXmust be a positive integer less than or equal to 2147483647: 1, 2, 3, …, 2147483647 -
TASK_DATEshould follow the format ofYYYY-MM-DD. -
TASK_TIMEshould follow the format ofHH:mm.
Examples:
-
add 1 -tncall for meeting -td2021-12-03 -tt14:30Adds the taskcall for meetingwith date2021-12-03and time14:30to the task list of the 1st person listed. -
add 3 -tnEvening Run -td2022-01-05 -tt18:00 -taClementi ParkAdds the taskEvening Runwith date2022-01-05, time18:00and addressClementi Park.
Editing a task: edit
Edits an existing task in ContactSH.
Format: edit INDEX -tiTASK_INDEX [-tnTASK_NAME] [-tdTASK_DATE] [-ttTASK_TIME] [-taTASK_ADDRESS]
Notes:
- Edits a task attached to the person at the specified
INDEX.INDEXrefers to the index number shown in the persons list displayed.INDEXmust be a positive integer less than or equal to 2147483647: 1, 2, 3, …, 2147483647 - The tasks edited is specified by the
TASK_INDEX.TASK_INDEXrefers to the index number shown in the task list displayed.TASK_INDEXmust be a positive integer less than or equal to 2147483647: 1, 2, 3, …, 2147483647 - Existing values will be updated to the input value. *At least one of the optional fields must be provided.
-
TASK_DATEshould follow the format ofYYYY-MM-DD. -
TASK_TIMEshould follow the format ofHH:mm.
Examples:
-
edit 3 -ti2 -tnGroup Project MeetingChanges the name of the 2nd task attached to the 3rd person in the list toGroup Project Meeting. -
edit 2 -ti3 -tnPresentation Meeting -taZoomChanges the 3rd task of the 2nd person in the list. Name and address of the 3rd task is changed toPresentation MeetingandZoomrespectively.
Deleting a task: rm
Deletes a task attached to a specified person.
Format: rm INDEX -tiTASK_INDEX…
Notes:
- Deletes a task attached to the person at the specified
INDEX.INDEXrefers to the index number shown in the persons list displayed.INDEXmust be a positive integer less than or equal to 2147483647: 1, 2, 3, …, 2147483647 - The task deleted is specified by
TASK_INDEX.TASK_INDEXrefers to the index number shown in the task list displayed.TASK_INDEXmust be a positive integer less than or equal to 2147483647: 1, 2, 3, …, 2147483647. If the sameTASK_INDEXis specified more than once, the task will only be deleted once. - Multiple tasks of one person can be deleted in one command.
Examples:
-
rm 2 -ti2Deletes the 2nd task attached to the 2nd person listed. -
rm 1 -ti2 -ti3Deletes the 2nd and 3rd task attached to the 1st person listed.
Viewing list of tasks of a person: cat
Shows you a list of tasks that has been attached to a specific person.
-
Displays the list of tasks attached to the person at the specified
INDEX.Format:
cat INDEXNotes:
-
INDEXrefers to the index number shown in the displayed person list. -
INDEXmust be a positive integer less than or equal to 2147483647: 1, 2, 3, …, 2147483647
Examples:
-
cat 1Displays the list of tasks attached to the 1st person.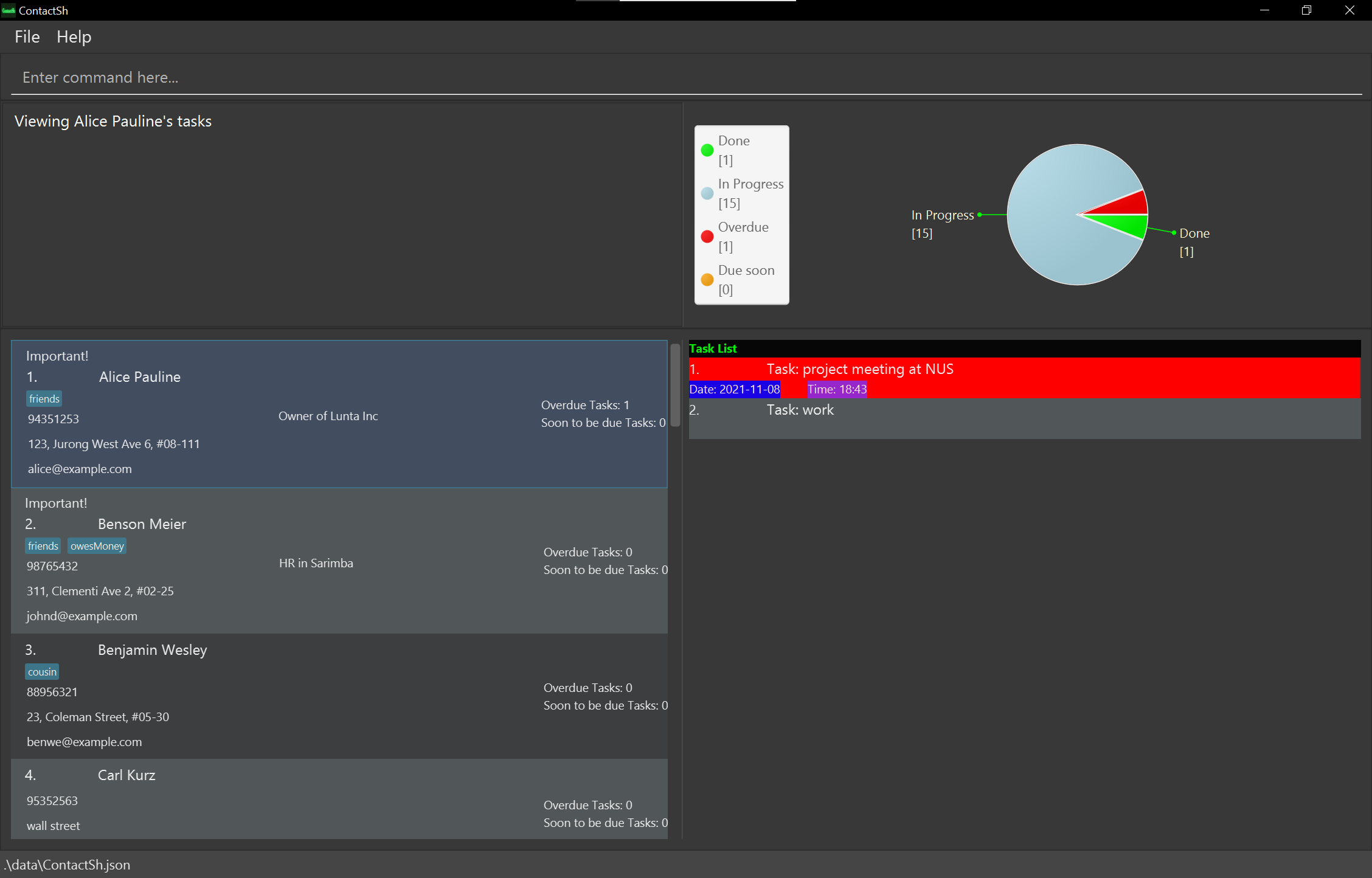
-
-
Displays a filtered list of tasks that has been attached to a specific person.
Format:
cat INDEX -f KEYWORDS…Notes:
- Displays a filtered lists of tasks for a specific person according to the keywords provided.
- Only tasks that matches the keywords will be shown. A task matches the keywords if the task name contains a word that starts with any of the
KEYWORDS. - A space is necessary between the flag and the keywords.
-
- Only one flag is allowed per command. e.g.
cat 1 -f workis fine, butcat 1 -f work -f nuswill search with the keywords “work -f nus”.
- Only one flag is allowed per command. e.g.
Examples:
- Alex is the first person in the person list and has the tasks [Work, project meeting at NUS].
cat 1 -f workwill display the task “work” -
cat 1 -f workDisplays the list of tasks attached to the 1st person that match the given keywords(s).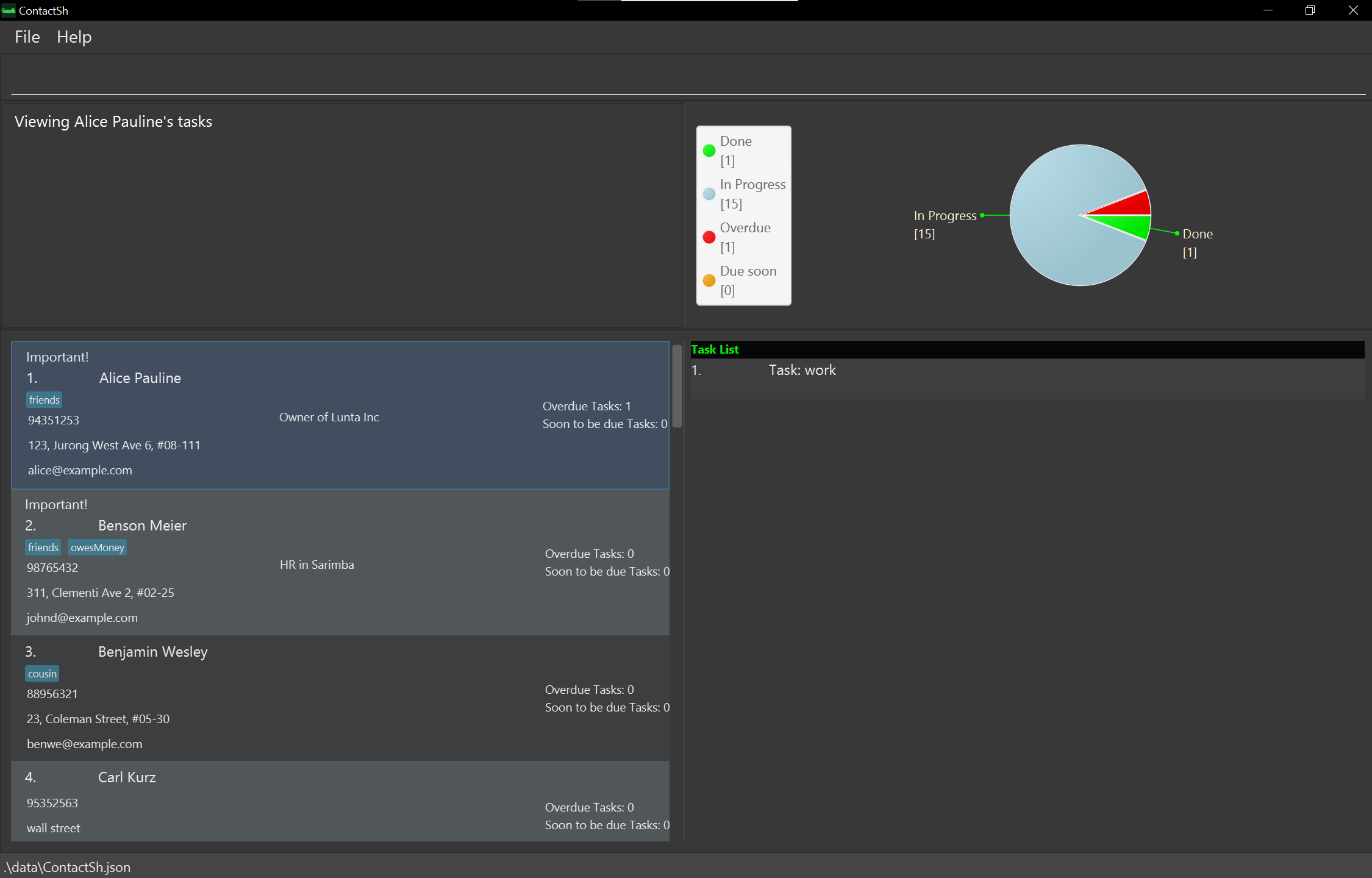
cat 1 -f work will match a task with the name
“Work at 5pm”. However, cat 1 -f ork and `cat 1 -f 5pm work” will not match the same task with the name “Work at 5pm”.
-
Displays the task list of all persons in ContactSH.
Format:
cat -AExample:
-
cat -A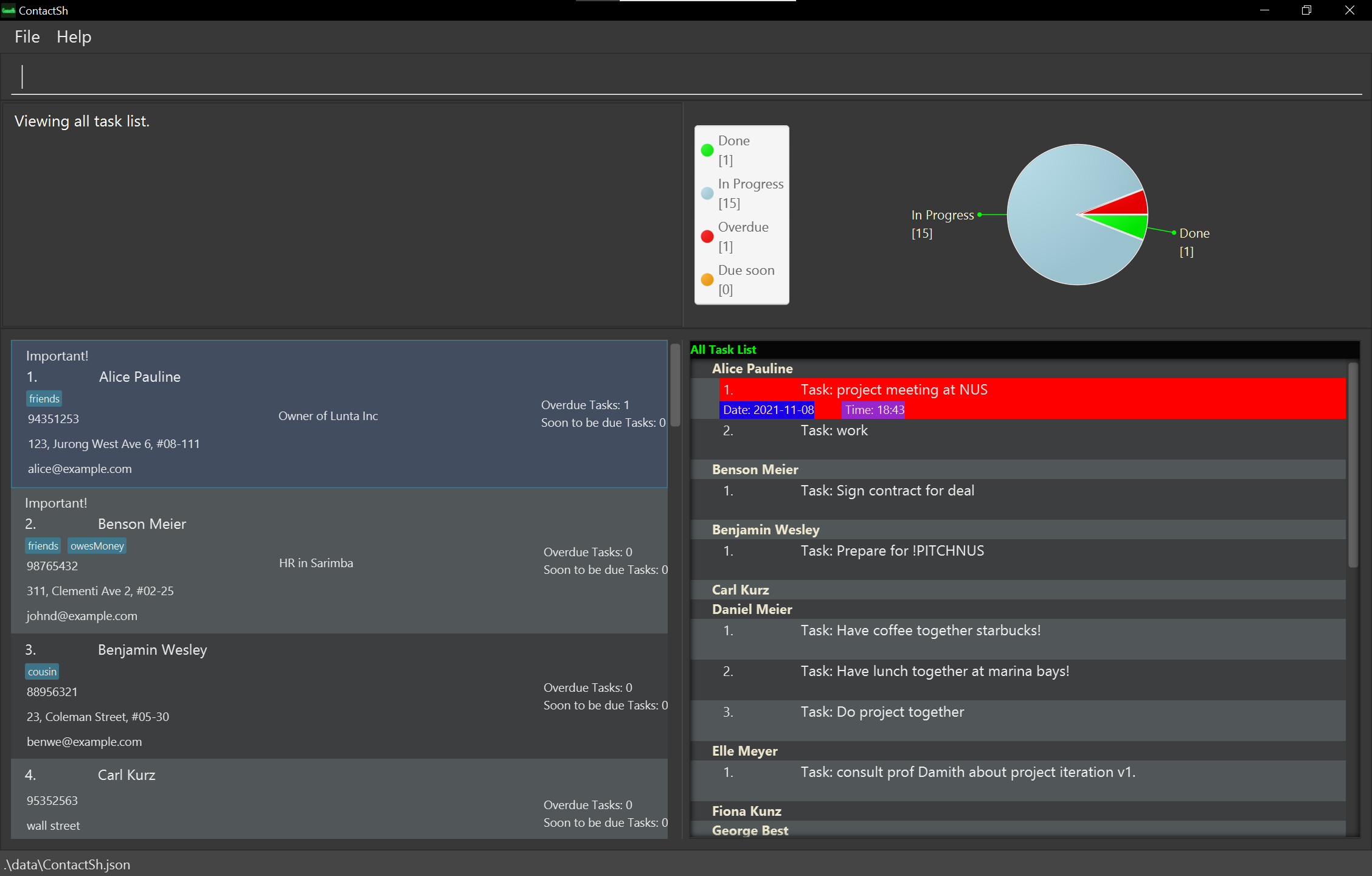
-
Marking a task as done: donetask
Marks an existing task in ContactSH as done.
Format: donetask INDEX -tiTASK_INDEX…
Notes:
- Marks tasks attached to the person at the specified
INDEXas done.INDEXrefers to the index number shown in the displayed person list.INDEXmust be a positive integer less than or equal to 2147483647: 1, 2, 3, …, 2147483647 - The tasks marked is specified by the
TASK_INDEX.TASK_INDEXrefers to the index number displayed in the tasklist of said person.TASK_INDEXmust be a positive integer less than or equal to 2147483647: 1, 2, 3, …, 2147483647 - Multiple tasks of one person can be marked as done in one command.
Examples:
-
donetask 4 -ti1 -ti5Marks the 1st and 5th task of the 4th person in the list as done.
Marking a task as not done: undotask
Marks existing tasks in ContactSH as not done.
Format: undotask INDEX -tiTASK_INDEX…
Notes:
- Marks tasks attached to the person at the specified
INDEXas not done.INDEXrefers to the index number shown in the displayed person list.INDEXmust be a positive integer less than or equal to 2147483647: 1, 2, 3, …, 2147483647 - The tasks marked is specified by the
TASK_INDEX.TASK_INDEXrefers to the index number displayed in the tasklist of said person.TASK_INDEXmust be a positive integer less than or equal to 2147483647: 1, 2, 3, …, 2147483647 - Multiple tasks of one person can be marked as not done in one command.
Examples:
-
undotask 4 -ti1 -ti5Marks the 1st and 5th task of the 4th person in the list as not done.
Setting the number of days before tasks are considered due soon: reminder
-
Displays the current number of days prior to the date of tasks for them to be considered due soon.
Format:
reminderNotes:
- The default value is 3 days.
-
Sets the number of days prior to the date of tasks for them to be considered as due soon. This affects all tasks.
Format:
reminder -s DAYSNotes:
-
DAYSrefer to the number of days prior to a task’s date. The day must be a positive integer less than or equal to 2147483647: 1, 2, 3, …, 2147483647 - All tasks share the same number of days before it is considered as due soon.
- A space is necessary between the flag and
DAYS.
Example:
-
reminder -s 10All tasks that are due within a 10-day period from the current system date will be considered due soon.
-
Clearing the screen: clear
Clears the persons list and task list displayed. Does not delete any persons or tasks.
Format: clear
Example:
-
clearClears the persons list and task list in the GUI
Accessing the cache
-
ContactSH guarantees it saves up to the last 25
commands(both valid and invalid) that you input. You can browse through the previous input using the up and down arrow key on your keyboard when typing in the command box. -
ContactSH may save up to 50 newest
commands. However, once the cache is full, half (25) of the oldestcommandwill be deleted. Hence, the oldest 25commandsis not guaranteed to be saved. -
Cache will be emptied once you end the session (the application is closed). Hence,
commandsfrom previous sessions cannot be retrieved.
Saving the data
- ContactSH data are saved in the hard disk automatically after any command that changes the data. There is no need to save manually.
Editing the data file
- ContactSH data are saved as a JSON file
[JAR file location]/data/contactsh.json. Advanced users are welcome to update data directly by editing that data file.
Archiving data files [coming in v2.0]
Details coming soon …
FAQ
Q: How do I transfer my data to another Computer?
A: Install the app in the other computer and overwrite the empty data file it creates with the file that contains the data of your previous ContactSH home folder.
Command summary
| Action | Format, Examples |
|---|---|
| Add |
add -nNAME -pPHONE_NUMBER -eEMAIL -aADDRESS [-dDescription] [-lLABEL]… e.g., add -nJames Ho -p22224444 -ejamesho@example.com -a123, Clementi Rd, 1234665 -dRich -lfriend -lcolleague
|
| Clear | clear |
| Delete |
rm INDEXe.g., rm 3
|
| Edit |
edit INDEX [-nNAME] [-pPHONE_NUMBER] [-eEMAIL] [-aADDRESS] [-dDescription] [-lLABEL]…e.g., edit 2 -nJames Lee -ejameslee@example.com
|
| Find |
find [-n NAME] [-p PHONE_NUMBER] [-e EMAIL] [-a ADDRESS] [-d Description] [-l LABEL] [-tn TASK_NAME]e.g., find -n Alex
|
| List | ls |
| Sort | sort [-r] |
| Help | man |
| Add Task |
add INDEX -tnTASK_NAME [-tdTASK_DATE] [-ttTASK_TIME] [-taTASK_ADDRESS] e.g., add 2 -tnCelebrate $1 million revenue -tnContact Professor to get help
|
| Delete Task |
rm INDEX -tiTASK_INDEX e.g., rm 2 -ti2 -ti3
|
| Edit Task |
edit INDEX -tiTASK_INDEX [-tnTASK_NAME] [-tdTASK_DATE] [-ttTASK_TIME] [-taTASK_ADDRESS] e.g., edit 1 -ti2 -tnInternship Interview -tt15:45
|
| Mark Task Done |
donetask INDEX -tiTASK_INDEX… e.g., donetask 3 -ti2 -ti5
|
| Undo Mark Task Done |
undotask INDEX -ti TASK_INDEX… e.g., undotask 3 -ti2 -ti5
|
| View Tasks |
cat INDEXe.g., cat 4cat INDEX -f KEYWORDSe.g., cat 4 -f workcat -A cat -A -f KEYWORDSe.g., cat -A -f work
|
| View Reminder Days | reminder |
| Set Reminder Days |
reminder -s DAYSe.g., reminder -s 21
|
Flag summary
| Description | Flag Formats | Input constraints |
|---|---|---|
| Name of Person | -n |
Name should consist of alphanumeric characters and spaces only. Cannot be blank. |
| Phone number of Person | -p |
Phone number should consist of numbers only. Minimum 3 digits long |
| Email of Person | -e |
Email should be of format local-part@domain. 1) The local-part should only contain alphanumeric characters and these special characters, +_.-. 2) The domain is made up of domain labels seperated by ..3) Each domain label must be at least 2 characters long, start and end with alphanumeric characters and can contain -. |
| Address of Person | -a |
Address can take any values, but must not be blank. |
| Description of Person | -d |
Description can take any values, but must not be more than 500 characters long. |
| Label of Person | -l |
Labels should consists of alphanumeric characters only. Cannot be blank. |
| Denotes if a Person is important | -impt |
Input should be true or false, case of the words does not matter. |
| Task Index of the Task | -ti |
Task Index should be a positive integer less than or equal to 2147483647: 1, 2, 3, …, 2147483647. |
| Name of the Task | -tn |
Task name should contain at least one non-whitespace character. |
| Date of the Task | -td |
Task date should follow the format: YYYY-MM-DD. |
| Time of the Task | -tt |
Task time should follow the format: HH:mm. |
| Address of the Task | -ta |
Task address should contain at least one non-whitespace character. |
Reverse flag for sort command |
-r |
-r flag does not take in any input and should be used as a standalone flag. |
All flag for cat command |
-A |
-A flag does not take in any input and should be used as a standalone flag. |
Filter flag for cat command |
-f |
-f flag can take in any number of inputs following a space between the flag and the inputs. |
| Number of days before a task is considered as due soon. | -s |
Number of days should be a positive integer less than or equal to 2147483647: 1, 2, 3, …, 2147483647. |